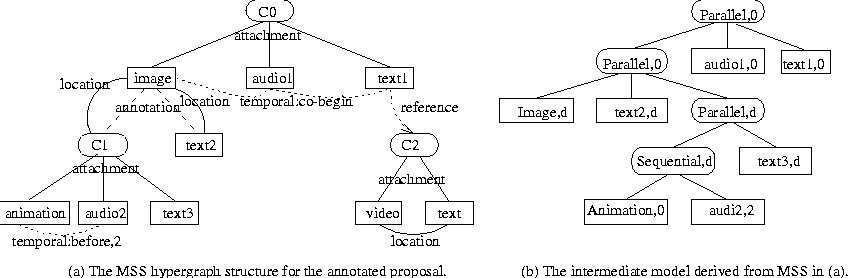
Figure: The MSS hypergraph structure and the intermediate model of the annotated medical report.

Figure: The MSS hypergraph structure and the intermediate model of the annotated
medical report.
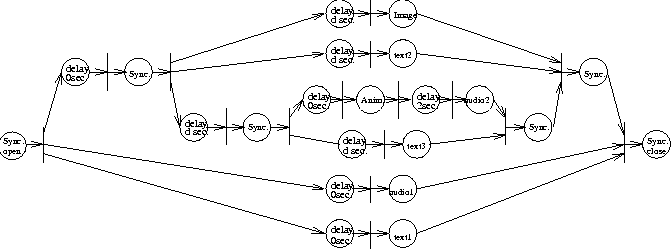
Figure: MDS derived from MSS shown in Figure 9.
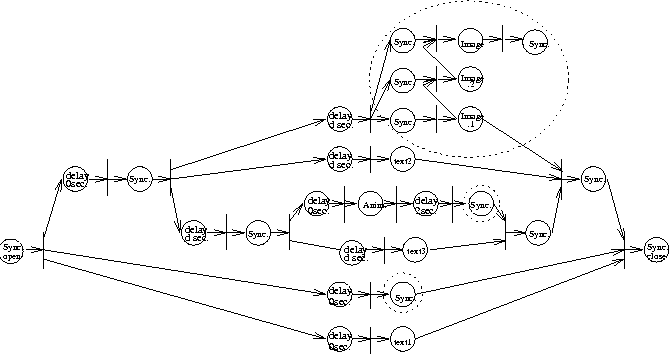
Figure: MCS derived from MDS shown in Figure 10. The places enclosed by dotted line represent
objects processed in the transformation.
A medical doctor Smith is preparing a report for his supervisor Kessler and
his group members Wang and Larson. His report C0 contains a text file of a
medical record, an audio memo recorded by himself, and a nuclear image of the
patient. The text also refers to a confidential
report C2 for his supervisor Kessler only.
Suppose Smith receives two annotations about the image in
his proposal. One annotation is a text while the other annotation C1
is composed of an animation, an
audio, and another text where the audio will start to play
two seconds after the animation has been played. Figure  (a)
shows the MSS of report C0
proposal which includes all the different types of nodes and links in
the hypergraph structure to specify the static structure of the multimedia objects.
The MSS modeled by the hypergraph structure can be transformed into the
corresponding MDS according to the MSS-to-MDS algorithm described in
Section 3.2.
Figure
(a)
shows the MSS of report C0
proposal which includes all the different types of nodes and links in
the hypergraph structure to specify the static structure of the multimedia objects.
The MSS modeled by the hypergraph structure can be transformed into the
corresponding MDS according to the MSS-to-MDS algorithm described in
Section 3.2.
Figure  (b) illustrates the intermediate model derived from the MSS.
The number after the comma in each node represents the value of the delay
attribute of the object.
Figure
(b) illustrates the intermediate model derived from the MSS.
The number after the comma in each node represents the value of the delay
attribute of the object.
Figure  is the MDS constructed from the intermediate model.
Suppose that the receiving end does not have audio device and the
bandwidth of the communication network is not enough to transmit the image
object unless the size of the image is reduced in order to obtain the
guarantee form the QOS manager. By applying Algorithm 2, MCS
is transformed from MDS by deleting the audio objects and then employing
progressive transmission on the image object.
The resulting MCS is shown in Figure
is the MDS constructed from the intermediate model.
Suppose that the receiving end does not have audio device and the
bandwidth of the communication network is not enough to transmit the image
object unless the size of the image is reduced in order to obtain the
guarantee form the QOS manager. By applying Algorithm 2, MCS
is transformed from MDS by deleting the audio objects and then employing
progressive transmission on the image object.
The resulting MCS is shown in Figure  in which
a two-level progressive transmission is applied on the image object, where
image.1
is an image of a lower resolution to be transmitted first while image.2
and image are the data to be transmitted progressively in order
to fill up the detail of the original nuclear image.
Optimization is possible to reduce the complexity of the G-Net of an MDS.
Various heuristics can be devised based on properties of the application.
Figure
in which
a two-level progressive transmission is applied on the image object, where
image.1
is an image of a lower resolution to be transmitted first while image.2
and image are the data to be transmitted progressively in order
to fill up the detail of the original nuclear image.
Optimization is possible to reduce the complexity of the G-Net of an MDS.
Various heuristics can be devised based on properties of the application.
Figure  shows an optimized version of MDS in this example by
deleting places with delay 0 and their output transitions.
shows an optimized version of MDS in this example by
deleting places with delay 0 and their output transitions.
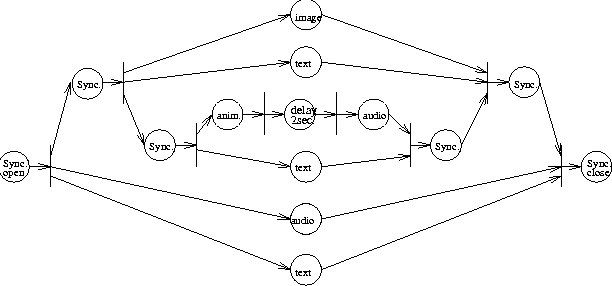
Figure: Optimized version of MDS shown in Figure 10.